Z-scheme catalyst for impurities in water developed by Chinese Researchers
In the last few years, accelerated industrialization has been the reason for more serious environmental pollution. One of the greatest threats to human health and critical risks to the ecosystem is antibiotics and microbiological contamination in water. As a result, efficient therapy has been an essential assignment for eliminating bacterial and antibiotic contamination from the watery atmosphere currently.
Lately, a research group including Professor Wu Zhengyan developed a unique Z-scheme photocatalyst to deal with impurities in water.
The research outcomes are released in the journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental titled as kinetics, reaction pathways, and mechanism investigation for improved environmental remediation by 0D/3D CdTe/Bi2WO6 Z-scheme catalyst.
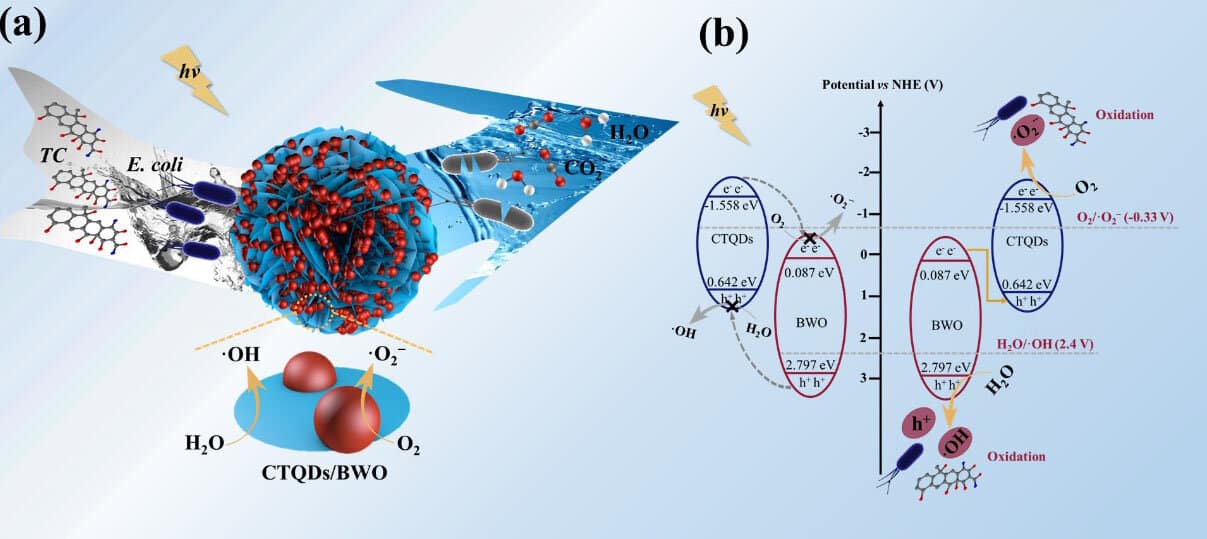
Profesor Zhengyan Wu and his doctoral scholar YANG Pengqi, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, explained how they utilized hydrothermal technique to prevaricate the Z-scheme photocatalyst, CdTe quantum dots/Bi2WO6 (CTQDs/BWO – Bismuth tungstate), which was made to improve photocatalytic performance.
Few highlights of the study were:
- A new Cadmium telluride quantum dots /Bismuth tungstate Z-scheme heterojunction was made.
- The Quantum effect of Cadmium telluride quantum dots improved the visible light absorption of the photocatalyst.
- The Z-scheme heterojunction improved photocatalytic E. coli inactivation and TC deterioration.
- The connection between the photocatalytic property and the material structure was assessed by DFT.
As the quantum effect substantially increased the shift of charge-carriers in the interface of Bismuth tungstate and Cadmium telluride quantum dots, this photocatalyst displayed much greater photoinactivation effectiveness of Escherichia coli and photodegradation effectiveness of TC as opposed to the pure Bismuth tungstate under the visible light.
This research opens a distinct path to develop highly efficient Z-scheme photocatalysts and displays an encouraging possibility for practical application.
The study team included PengqiYang, ChaowenChen, DongfangWang HuanMa, YueDu, DongqingCai, XinZhang, and ZhengyanWu.
The study was backed by the Science and Technology Service Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Key R&D Program of Ningxia Province, and the National Key R&D Program of China.
Z-scheme catalyst for impurities in water developed by Chinese Researchers