Novel method converts methane in natural gas to methanol at room temperature
Scientists at the University of Illinois, Chicago, have found a method to transform the methane in natural gas into liquid methanol at room temperature.
The results of the study are reported in the journal PNAS. This novel discovery might potentially provide a cleaner power source for a number of our day-to-day activities.
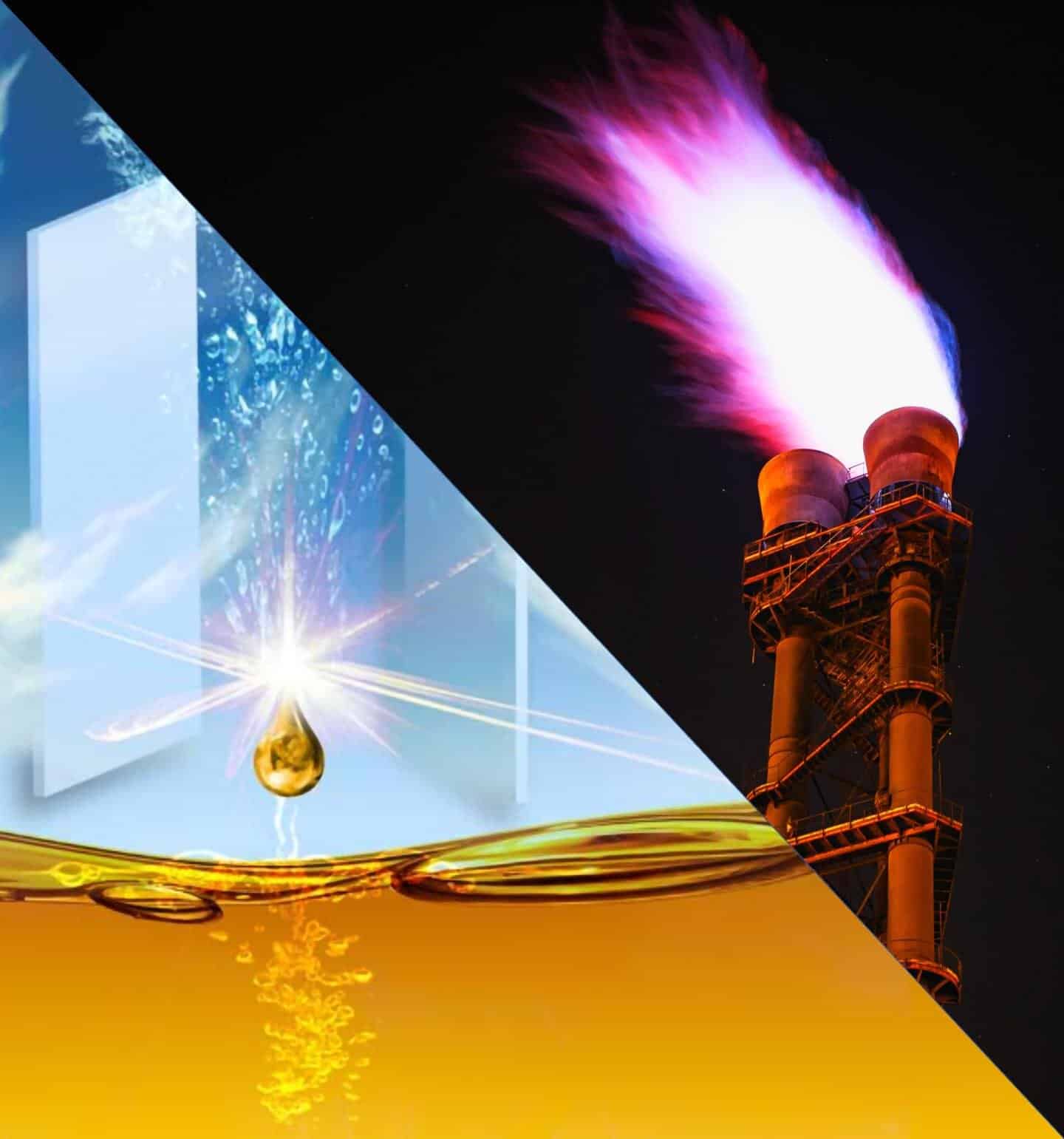
Natural gas produces a powerful greenhouse gas – carbon dioxide when burned.
As per reports from the U.S Energy Information Administration, in 2019, the U.S. used around 31 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, adding around 1.6 gigatons of CO2 to the environment.
Transforming natural gas to methanol, a liquid fuel that burns a lot more cleanly and can be utilized to produce plastics and gasoline, will a more reliable method to utilize natural gas. However, transforming the methane present in natural gas into methanol needs a lot of heat and pressure and produces a considerable amount of CO2.
Meenesh Singh, assistant professor, chemical engineering, the UIC College of Engineering
, and co-author of the study, stated that scientists have worked on methods to transform methane to methanol at room temperature levels to avoid all the heat and pressure that is presently needed in commercial procedures to carry out this transformation.Additionally, methanol is believed to be the “fuel in the future,” driving a “methanol economic climate” where it substitutes fossil fuels in transportation, power storage, and the leading precursor material for synthetic chemicals and various other items. Meenesh Singh stated that presently, methanol is utilized in fuel cell technology that powers few city buses and other transports. Its less emission potentials and greater volumetric energy density make it an eye-catching option for fossil fuels.
He further stated that besides being a cleaner-burning gas, methane could likewise be stored securely in normal containers, unlike natural gas, which has to be kept under pressure and which is far more costly.
Large amounts of heat and pressure are needed to break the hydrocarbon bonds in methane gas, the initial process in methanol production. However, Meenesh Singh and Aditya Prajapati, UIC graduate students, have actually determined a catalyst product that assists in lowering the energy required to break these bonds to ensure that the reaction can take place at room temperature.
Prajapati stated that they had lowered the manufacturing process’s temperature level from over 200oC to room temperature, which is around 20oC.
Their catalyst is made up of copper and titanium. The catalyst, along with a small amount of electrical power, promotes breaking the hydrocarbon bonds of methane and methanol production. The method utilizes less energy than standard techniques, and as it does not need equipment for producing high pressure and heat, it can be set up swiftly and economically.
Meenesh Singh stated that their procedure does not need to be streamlined. It can be executed in a place as small as a van and is compact for a distributed usage of natural gas and methanol production.
Meenesh Singh and his co-workers have actually submitted a provisional patent for the procedure and assume that it can transform a few liters of methanol per day.
Novel method converts methane in natural gas to methanol at room temperature
Also Read: