Clinical Pharmacy Career Opportunities
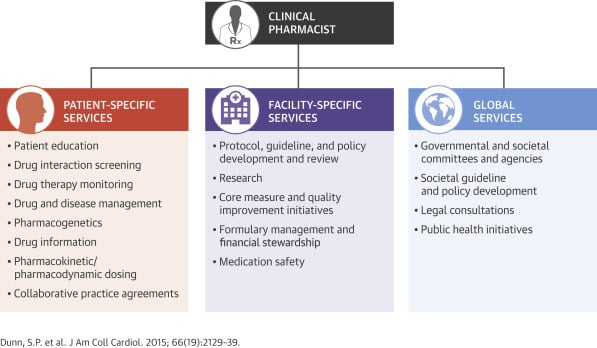
The branch of pharmacy dealing with patient care and medication, promoting health and wellness is known as the clinical pharmacy. The field of clinical pharmacy can be defined as the area of pharmacy that deals with the science and practice of using medication rationally. The pharmacist working in this field works in management with the doctors for patient healthcare and consists of various services. In any setting wherever medicines are prescribed and used, clinical pharmacists can provide services, such as home-based care services, community pharmacies, clinics, nursing homes, and pharmacists practicing in hospitals. The term “clinical” defines the type of activity that is connected to the health of the patients and does not necessarily suggest an action implemented in a hospital setting only. Clinical pharmacy activities can also be carried out by hospital pharmacists and community pharmacists.
Clinical pharmacists have a wide range of opportunities to pursue a career in this field. A clinical pharmacist can either provide general clinical services or can specialize in a particular area and provide specialized services.
Educational Requirements: The qualifications required to have a career in clinical pharmacy include a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) degree, along with one or more
years of post-graduate training M.Pharm (Pharmacy Practice). Clinical pharmacists have substantial education in the pharmaceutical, biomedical, clinical, and socio-behavioral sciences.Skills Required:
Clinical pharmacists must have a certain set of skills in order to fulfill their job responsibilities and requirements.
- Patient Care Skills
- Pharmacy Staff Skills
- Drug Therapy Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Analytical Skills
- Communication skills
- Computer Skills
- Leadership Skills
- Research Skills
- Able to work together with other healthcare professionals
Clinical Pharmacy Career Opportunities
One can choose a career in a clinical pharmacy involving a subspecialty or can pursue a generalized clinical career. At any time during one’s career, a pharmacist can choose to specialize within a certain area.
The versatility and variety of a clinical pharmacy career can be seen from the available specialties in which clinical pharmacists may choose to practice, such as:
- Ambulatory Care: Clinical practice and patient care to a vast patient population with an array of chronic disease states is improved in a variety of practice settings such as the physician offices, community clinics, Veteran’s Affairs Medical Centers, and outpatient hospitals.
- Critical Care: For acutely ill patients with continuously changing organ function, the pharmacist will be associated with developing optimum, patient-specific pharmacotherapy routines as a critical care pharmacy provider.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: This involves pharmaceutical or biotechnology companies for outcomes-based research, and sales and marketing via education, through which patient care is improved.
- Clinical Administration: Involves improving patient care indirectly by using strong organizational, management, and operational skills as this area focus on a management role in pharmacy practice or academia.
- Drug Information: This area involves developing evidence-based suggestions about drugs and drug therapy for assisting in therapeutic policy management and patient care decisions. It involves specialty training to recover, examine, and communicate information efficiently.
- Pharmacy Informatics: A pharmacy informaticist uses clinical decision-making tools and evidence-based medicine for developing systemized approaches to patients combining health information and communications technology.
Other specialties in which clinical pharmacists may practice include areas like Emergency Medicine, Managed care, Adult Medicine, Infectious Diseases, Cardiology, Endocrinology/Diabetes, Immunology/Transplantation, Hematology/Oncology, Geriatrics, Pediatrics, Nutrition Support, Nephrology, Psychiatry and Central Nervous System, Poison Control, Women Health, and Outcomes and Economies.
Research-Oriented Clinical Pharmacy Career Opportunities:
In the healthcare sector, there is a vast growing demand for clinical pharmacist scientists for clinical research. Clinical scientists can analyze data for publication, design studies, and oversee clinical development strategies. Other areas include developing protocols for pharmacogenomics and biomarkers, and participation and leading preclinical studies on new technologies. The research setting in clinical research does not only involve a “lab-type” research setting but also consists of all phases of clinical trials, proof-of-principle projects, studies of human subjects with first-in-human, cohort, case-control, case-series, cross-sectional studies. Clinical pharmacists have various opportunities in Clinical Research such as – Clinical Safety Analyst, Clinical Research Coordinators (CRC), Clinical Research Scientist, Clinical Research Associates / Trial Monitor/ Clinical Monitor/ Field Monitor/, Regulatory Affairs Associates, Clinical Quality Assurance Auditor (CQA), Medical Science Liaison, Medical Writer, Clinical Data Management, among others.
Academia and Clinical Pharmacy Career Opportunities:
One of the many career opportunities of Clinical pharmacy is being a professor and lecture at a college of pharmacy. The clinical pharmacists who take teaching as their profession have dual roles: both as a professor of pharmacy and a clinical pharmacist. Specializing within a certain area of pharmacy, these pharmacists often work at a clinical site in the area where the academic institution is located. During the clinical rotations and other experiential training, several faculty members offer didactic instruction to students as well as serve as preceptors. A minimum of one year of residency is required to become a faculty member in most pharmacy colleges.
Clinical Pharmacy Career Opportunities Leadership Positions:
Opportunities to be a leader as a clinical pharmacist are greatly expanding as the role involves successfully influencing the behavior of pharmacy technicians, physicians, support staff, nurses, interns, and others for optimizing patient outcomes and improving medication safety.
Some of the Leadership Positions in Clinical Pharmacy include:
- Clinical Manager
- Clinical Pharmacy Operations Manager
- Clinical Pharmacist Specialist
- Clinical Coordinator
- Pharmacy Director
- Pharmacy Associate Director
- Pharmacy Assistant Director
- Pharmacy Supervisor
Within these roles, practitioners responsibilities include:
- Providing leadership through development and involvement in hospital quality initiatives, drug informatics, and clinical pharmacy consult services.
- In the Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, assisting in the development of a drug formulary and involvement.
- To physicians, nursing staff, other health care professionals, and professionals within the pharmacy setting, the leadership roles involve planning, developing and providing drug information and educational sessions.
- Precepting, teaching, and mentoring students.
An important step when deciding to become a clinical pharmacist is choosing the right major. Clinical pharmacists play an important role in patients’ healthcare as they are experts in the therapeutic use of medications within the healthcare system. Clinical pharmacists are a primary source of scientifically valid information and provide guidance regarding using medications in an appropriate, safe, and cost-effective way. In recent years, clinical pharmacists along with having access to clinics, hospitals, and educational institutes, are also making themselves more readily available to the public through a medication information hotline, reviewing medication lists, all in an effort to prevent future medication errors.
A career in clinical pharmacy is a highly reputed career as they determine if a medication plan is appropriate for their patient by using their knowledge of medication (including dosage, effectiveness, expense, drug interactions, side effects, etc.)