Scientists Discovered Methods To Transform Carbon dioxide Into Liquid Fuel
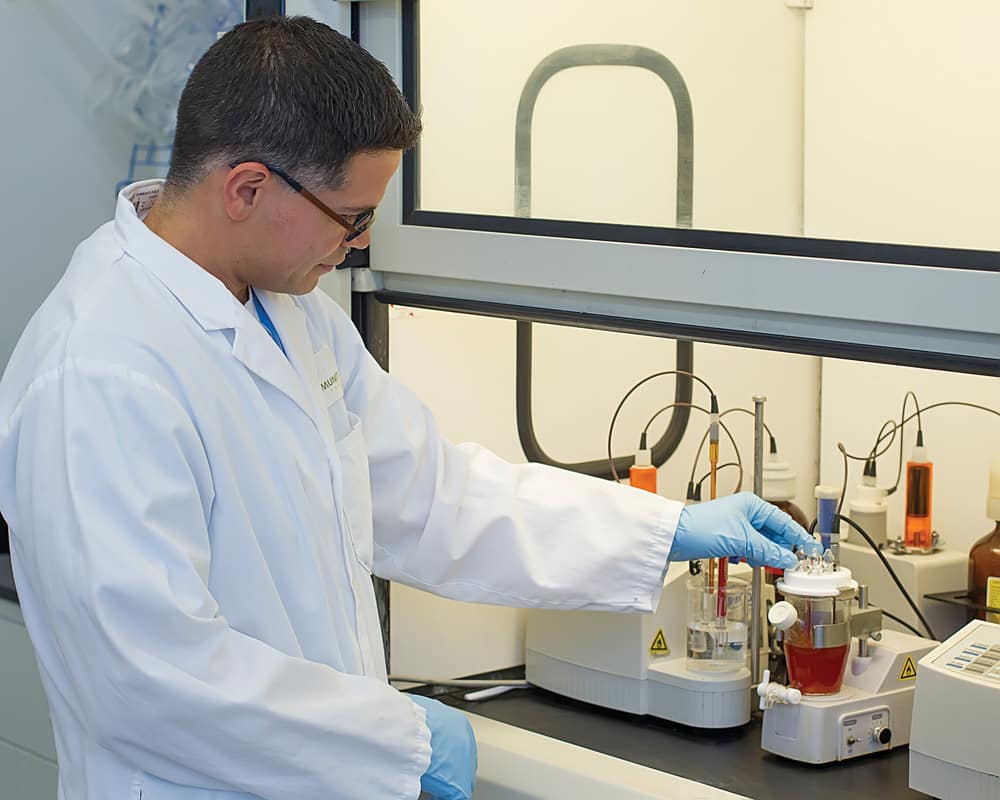
Chemical reactions are speeded up by catalysts and form the backbone of many industrial processes. For instance, catalysts are important in transforming heavy oil into jet fuel or gasoline. As of now, catalysts are associated with over 80% of all manufactured items.
A new electrocatalyst that converts carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into ethanol with very high energy efficiency, high selectivity for the desired final product and affordable price is developed by a research team, led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory in partnership with North Illinois University. Ethanol is a specifically preferable product as it is an active ingredient in almost all United States gasoline as well as is widely used as an intermediate item in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and chemical industries.
Di-Jia Liu, a UChicago CASE scientist in the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering, University of Chicago, and a senior chemist in Argonne’s Chemical Sciences and Engineering division said that the process resulting from our catalyst would add to the circular carbon economy, which involves the reuse of CO2. This method would certainly do so by electrochemically converting the carbon dioxide emitted from industrial
processes, such as alcohol fermentation plants or fossil fuel power plants into beneficial products at affordable prices.Atomically dispersed copper on carbon-powder support is present in the team’s catalyst. This catalyst breaks down carbon dioxide and water molecules by an electrochemical reaction, and under an external electric field, it precisely reconstructs the broken particles into ethanol. The “Faradaic efficiency” or electrocatalytic selectivity, of the process, is over 90%, much greater than any other reported process. Additionally, even at low voltage, the catalyst operates stably over the extended processes.
Tao Xu, a professor in physical chemistry and nanotechnology from Northern Illinois University said that that, with this research study, they have found a new catalytic system for converting CO2 and water into ethanol. The technique should likewise give a foundation for the development of highly effective electrocatalysts for CO2 conversion to a large array of value-added chemicals.
Transforming CO2 into various molecules is typically energy-intensive and expensive, as carbon dioxide is a stable molecule. But, according to Liu, utilizing their catalyst to the electric grid and make take advantage of the affordable electricity available from renewable sources like solar and wind during off-peak hours, they could pair the electrochemical process of CO2-to-ethanol conversion. As the process is carried out at a reduced temperature and pressure level, it can begin and stop swiftly in response to the intermittent supply of renewable electricity.
The group’s research took advantage of 2 DOE Workplace of Science User Facilities at Argonne – the Center for Nanoscale Materials, and Advanced Photon Source as well as Argonne’s Laboratory Computing Resource Center. Tao Li, an assistant professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Northern Illinois University and an assistant scientist in Argonne’s X-ray Science division said, thanks to the high photon flux of the X-ray beam of lights at the APS, we have captured the structural modifications of the catalyst during the electrochemical reaction. A reversible transformation from atomically dispersed copper to clusters of 3 copper atoms each on the application of a reduced voltage was exposed by this information together with high-resolution electron microscopy at CNM and computational modeling using the LCRC. The carbon dioxide to ethanol catalysis takes place on these little copper clusters. This research outcome is shedding light on ways to further boost the catalyst via rational design.
Liu said that utilizing this technique, they have prepared numerous new catalysts as well as found that they are all extremely efficient in transforming carbon dioxide to other hydrocarbons. They intend to proceed with this research study in partnership with the industry to advance this promising technology.
Scientists Discovered Methods To Transform Carbon dioxide Into Liquid Fuel
Author: Sruthi S