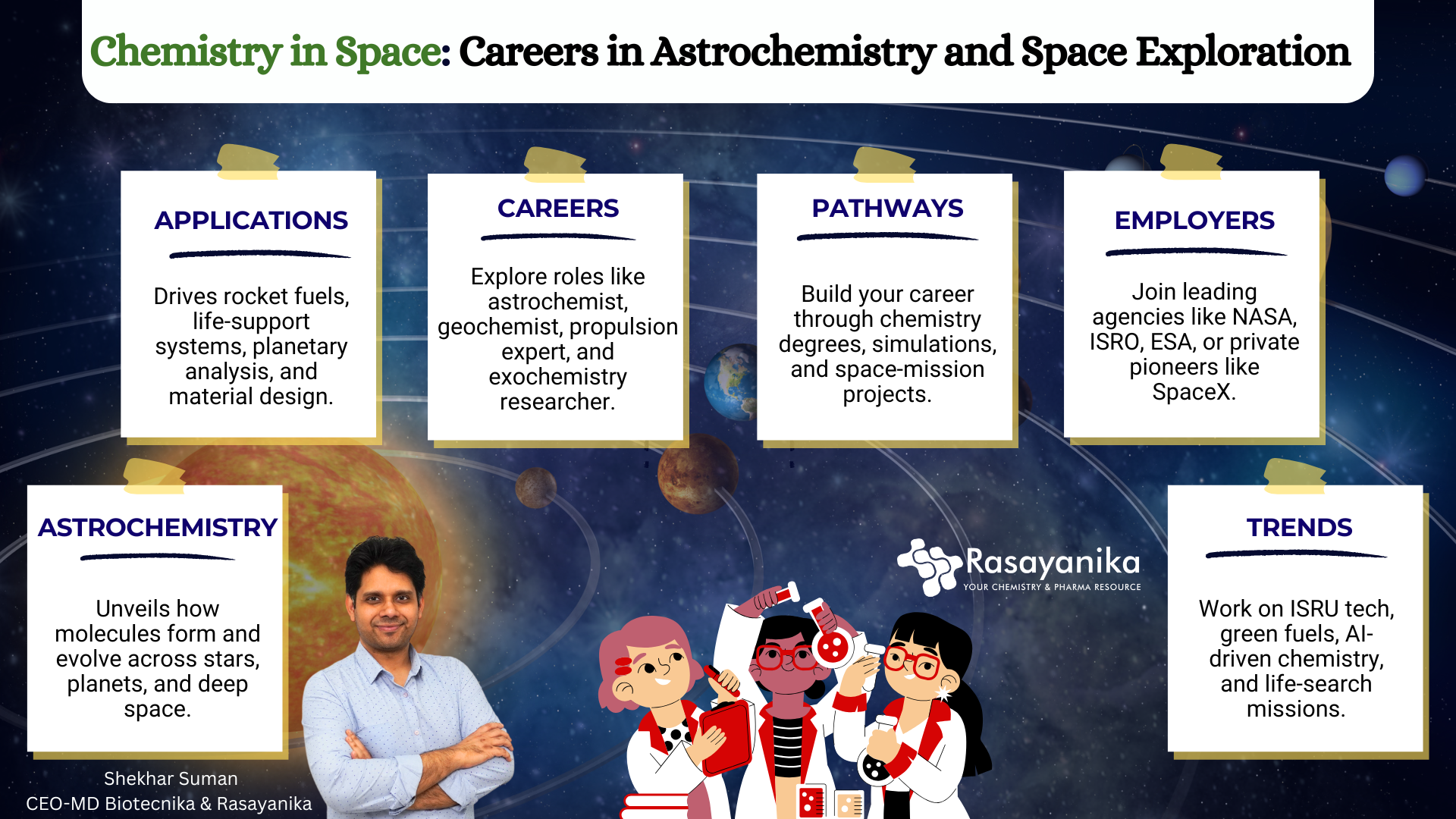
Chemistry in Space: Careers in Astrochemistry & Space Exploration
When you think of Space exploration, do visuals of rockets, planets, the solar system, or astronauts often come to your mind? But beyond these images and perceptions lies an often-overlooked driver of every mission’s success: Chemistry.
From detecting the presence of water on Mars to designing space life-support systems and analyzing the chemical fingerprints of alien atmospheres, Chemistry is essential. This is the domain of Astrochemistry, which is an evolving and dynamic field where molecules are becoming the messengers of the cosmos.
Have you ever gazed at the sky and thought about what lies beyond Earth, or are you fascinated and curious to know what happens at both the cosmic and molecular levels? Then you are closer to Space than you might think. Here, in this article, we’ll explore how Chemistry powers the Space journey beyond Earth and how you, with the right skills and passion, can build a career that reaches into the stars.
What is Astrochemistry?
Astrochemistry is an interdisciplinary field of Science that studies the interaction, evolution, as well as formation of Chemical compounds in Space. It merges the core principles of Physics and Chemistry with the enormity of Astronomy to answer questions such as:
- Could chemical processes give rise to life beyond our Earth?
- What Chemical molecules are present in the vacuum of Space?
- What is the reason behind the survival and formation of Chemical molecules in extreme environments?
Utilizing advanced and futuristic tools such as Mass Spectrometers, Quantum Chemistry simulations, as well as Radio and Infrared Telescopes, Astrochemists analyze and interpret everything from the atmospheres of distant exoplanets to the interstellar dust clouds. These understandings help us comprehend the chemical origins of Earth and other worlds.
Why Chemistry is Prime to Space Missions
Chemistry is the lifeline of Science and Space exploration, such as in:
- Life Support Systems: Space missions depend on closed-loop Chemical systems for life sustenance. Chemistry plays an essential role in Oxygen regeneration, CO₂ scrubbing, and water recycling aboard spacecraft, such as the ISS (International Space Station), making long-duration spaceflight possible.
- Rocket Propulsion: Rocket fuels are designed utilizing high-energy Chemical reactions. Liquid oxygen and Hydrogen, emerging Green fuels, as well as solid propellants are all the domain of Propulsion Chemists and Chemical Engineers. These Chemical formulations should be efficient, robust, and stable enough to escape Earth’s gravity.
- Space Materials: The materials in Space must endure vacuum, temperature fluctuations, as well as extreme radiation. Chemical Engineers develop ceramic coatings, heat shields, and radiation-resistant polymers that protect astronauts and spacecraft.
- Sustainable Space Farming: Future Planets and Moon Space bases would require Bioregenerative life-support systems. Chemistry would play a critical role in producing fertilizer from the soil present on the planet (such as that of Martian soil), supporting plant and life growth in space habitats, as well as converting waste materials into beneficial nutrients.
- Planetary Exploration: The orbiters and rovers carry advanced instruments that analyze and detect Chemical signatures in Space. For example, one of NASA’s (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) rovers, “Perseverance,” utilizes tools such as X-ray fluorescence analyzers and Raman Spectrometers to search and explore organic and chemical molecules on Mars.
Hence, Chemistry makes Space exploration survivable, sustainable as well as efficient.
Careers in Astrochemistry & Space Exploration
If you are enthusiastic about careers in Astrochemistry & Space Exploration, then here’s how you can make your dreams come true and excel in your career:
- Planetary Geochemist
- Focus: They analyze rock, atmospheric, and soil samples from moons and planets
- Notable Missions: Mars rovers and Lunar sample analysis
- Skills: Mass Spectrometry, Mineralogy, and Isotope Analysis
- Astrochemist
- Focus: They study molecules in Space, examining how molecules form, influence, as well as evolve planet and star formations.
- Workplaces: ESA (European Space Agency), NASA, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), and Academic institutions
- Tools: Chemical Modeling, Telescope Data Analysis, and Spectroscopy
- Propulsion Chemist
- Focus: They develop as well as refine rocket fuels for Space Launch Systems.
- Trend: Eco-friendly propellants (such as Ionic liquids and Hydroxylammonium Nitrate)
- Employers: Blue Origin, SpaceX, and IPRC (ISRO Propulsion Complex)
- Space Instrumentation Chemist
- Focus: They calibrate and design Analytical tools utilized in space missions.
- Examples: MOMA on ExoMars and ChemCam on Curiosity
- Skills: Systems Engineering, Data Analysis, and Instrumentation
- Life-Support Chemist
- Focus: They develop self-sustaining environmental systems for space habitats.
- Applications: deep-space missions, Mars/Moon bases.
- Tasks: Microbial control, air revitalization, and Water recovery.
- Exochemistry Researcher (Astrobiology Focus)
- Focus: They explore how organic molecules form in space-like conditions, such as the formation of amino acids.
- Projects: Interstellar ice and simulations of cometary under cosmic radiation.
- Impact: Advances the search for life beyond Earth.
These exciting roles offer exciting frontiers not just in discovery but in building the foundation of future space civilization
Skill & Academic Roadmap
You do not require a spacesuit to work in Space Science. Here’s how to get your career started:
- Education:
- Bachelor’s: Chemical Engineering, Physics, and Chemistry
- Master’s/PhD: Specializations in Space Sciences, Astrochemistry, Planetary Geology, or Materials Chemistry.
- Institutions to consider:
- India: IITs (Indian Institute of Technology), IISc (Indian Institute of Science), ISRO Space Applications Centre, PRL (Physical Research Laboratory), and IUCAA (Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics)
- Global: Harvard-Smithsonian CfA, Caltech, MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), University of Arizona, Leiden University
- Key Skills To Learn:
- Radiochemistry, Quantum Chemistry, and Spectroscopy
- Thermodynamics and Analytical Chemistry
- Simulation software: MATLAB, Python, AstroPy, and Gaussian
- Data Analysis: Handling mission Datasets from space probes and satellites
- Communication: Presenting Research papers at conferences and writing Research papers
- Sample Projects:
- Study the degradation of polymers under vacuum and UV (ultraviolet) in laboratory conditions.
- Analyze Mars rover spectroscopy Data (such as from NASA’s PDS archive)
- Simulate Chemical reactions in icy interstellar environments
The Opportunities
Astrochemistry is no longer a niche field; it’s becoming increasingly mainstream. Institutions hiring professionals worldwide are:
- ISRO – PRL, Human Spaceflight Centre, IIST (Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology), IPR
- NASA – Goddard Space Flight Center, Ames Research Center, and JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory)
- CNSA & JAXA – Japan’s Hayabusa2 and China’s Moon and Mars missions
- ESA – Rosalind Franklin Rover (ExoMars) and JUICE (JUpiter ICy Moons Explorer)
- Academia – Mission collaborations, teaching positions, and Research fellowships
- Private Sector – Rocket Lab, Axiom Space, Blue Origin, and SpaceX
Internships and Fellowships, including SERB-TARE, ISRO YUVIKA, and NASA Pathways, offer excellent opportunities for Space Chemistry aspirants.
Emerging Trends in Astrochemistry
Astrochemistry is evolving with these cutting-edge developments:
- AI-Enhanced Chemistry: Machine Learning (ML) models predict how unknown chemical or organic molecules will behave in extraterrestrial environments, thereby reducing trial-and-error laboratory work and speeding up reaction modeling.
- ISRU (In-Situ Resource Utilization): Utilizing local resources, such as extracting oxygen from Martian CO₂ or Lunar regolith for fuel and life support. Chemists are developing systems for the purification, transformation, and extraction of resources.
- Biosignature Detection: With missions like Europa Clipper and Dragonfly, Chemists are developing sensitive instruments to detect signs of life in subsurface oceans and icy terrains.
- Prebiotic Chemistry in Space: Understanding how life’s ingredients, i.e., sugars, amino acids, or nucleobases, form under cosmic conditions informs both Earth’s early Chemical History and Astrobiology.
- Green Propulsion: The shift toward safer and eco-friendly fuels is urgent. Chemists are researching alternatives to hydrazine-based fuels, like hydrogen peroxide blends and ionic liquids.
Final Thoughts: Your Molecules, Their Mission
In a universe filled with nebulae, planets, and stars yet to be explored, Chemistry is the key to understanding and gaining insights into it all. Astrochemistry lets us understand some of the most profound questions humanity has ever faced: Where did we come from? Can we survive beyond Earth? Are we alone?
For those driven by curiosity and excitement, Chemistry offers great careers in Astrochemistry & Space Exploration that takes to the stars and moon. You won’t need to leave Earth to be part of the next giant leap; you just need to follow the molecules.
So, are you ready to turn your passion for Chemistry into a career in Science?















































too good