Table of Contents
Plant-Based Immunomodulators: Phytochemical Insights from Natural Materials
Did you know that from ancient times, long before any hospitals or pharmaceuticals existed, people used to rely on plant extracts as their primary source of medicine, which they used to collect from forests, fields, and even home gardens. Ancient civilizations did not know the concept of immunomodulation, but they were indirectly following the principles, such as applying turmeric paste on wounds, skin infections, and consuming the extract with warm milk to treat fever or cold. Holy Basil leaves were consumed directly or in herbal fusions or decoctions against cough, fever, or respiratory diseases, etc.
Ancient practices like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese medicine used plant extracts and plant materials to regulate our immune system, even without understanding the science behind it.
Today, the advanced medications and drug systems depend on plant extracts because they are eco-friendly, more reliable, natural, and safer compared to synthetic molecules. The plants have natural immunomodulators that are suitable for a long time and yet safe.
By studying the phytochemistry of the plants , we can discover more bioactive compounds that can interact with the immune system, and this would support the development of effective plant-based medicines and therapies.
In this article, we will discuss how phytochemicals of different plant materials are responsible for immunodulatory effects in our body.
What is an Immunomodulator?
An Immunomodulator is any substance or agent that has the ability to influence the activity of the immune system. They can be of the following types:
- Immunostimulatory
- Immunosuppressive
- Immunoregulatory
They can be a drug or a compound made up naturally or synthetically that can modify or regulate the activity of the immune cells. E.g, Plant extracts such as mentioned above, turmeric, holy basil, and others have certain type of phytochemicals that influences the signalling pathways, immune cells, and cytokines to maintain our immune system.
Role of Plants as Natural Immunomodulators
Medical Plants have bioactive phytochemicals that were used to regulate and maintain our immune system for centuries in Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine, and in ethnobotany long before the concept of immunomodulatory.
Advantages of plant-derived immunomodulatory compounds
- Biocompatibility
The bioactive compounds collected from plants are generally safe with very low toxicity, allowing them to be used for long-term use with fewer side effects.
- Structural diversity and Phytochemistry
Phytochemicals such as flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, etc, can target multiple signalling pathways of the immune system.
- Synergistic effects
In a single plant, multiple bioactive compounds work together, which enhances the immunomodulatory response more than isolated molecules.
Phytochemical Basis of Immunomodulatory Activity
Phytochemistry is the study of chemical compounds produced by plants. In this study, the main objective is to search for bioactive compounds among phytochemicals that influence human health. Phytochemistry is vital for immunomodulatory activity because the compounds interact and affect signalling pathways to stimulate, suppress, or balance responses of immune cells.
Major classes of immunomodulatory phytochemicals:
- Alkaloids: These are nitrogen-containing compounds, such as piperine, that can regulate the activity of macrophages and modulate the production of cytokines.
- Flavonoids: The compounds such as quercetin and kaempferol contain polyphenols and are used as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory substances.
- Terpenoids: These are compounds that can influence both innate and adaptive immunity, e.g, ginsenosides, andrographolide, etc.
- Polyphenols: They support immune cell function andmodulate inflammatory pathways.
- Saponins: These are compounds that contain glycosides and have the ability to enhance antibody production, and are used as vaccine adjuvants.
- Polysaccharides: They activate macrophages, natural killer cells, and other innate immune responses, e.g, Macromolecules like beta-gulans and pectins, etc.
Plant Materials with Proven Properties
Many plant materials have been studied for their immunomodulatory properties. A few common plants are mentioned below in the table, along with their bioactive compounds that can suppress, enhance, or balance immune responses.
|
Medicinal Plant |
Key Bioactive Compounds | Immunomodulatory Uses |
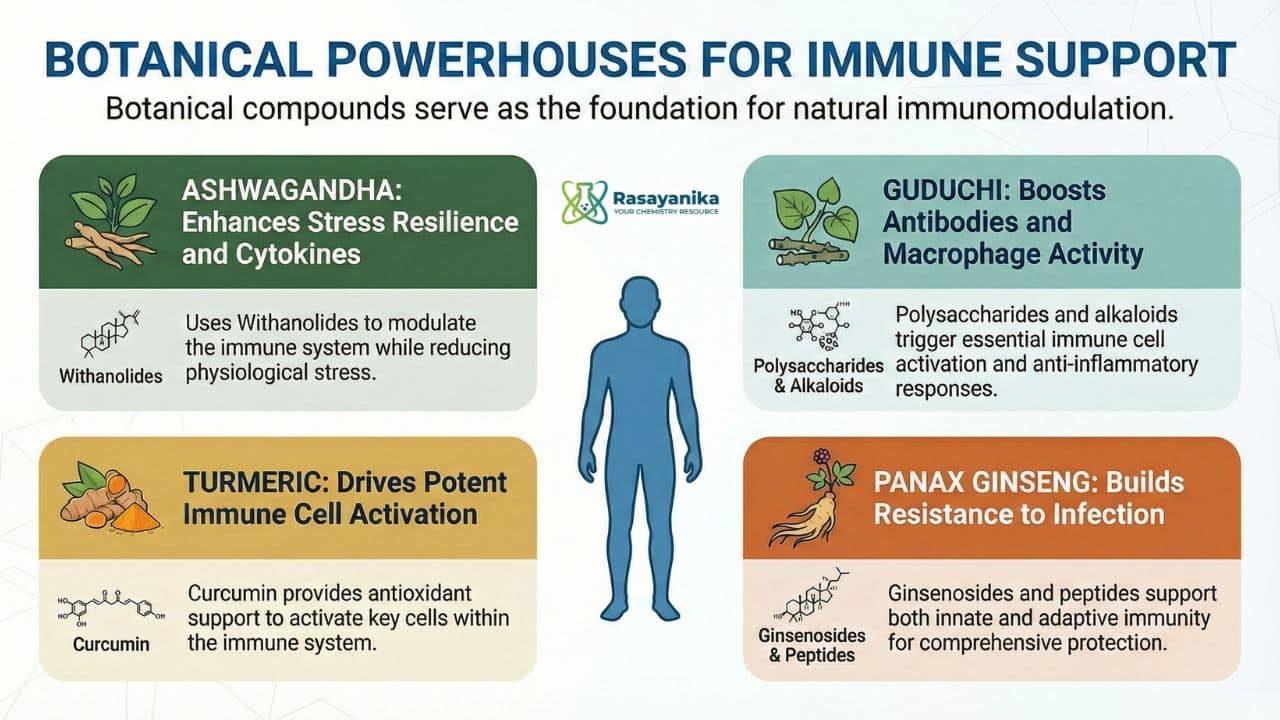
| Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) | Withanolides, sitoindosides, alkaloids | They can enhance immune response, reduce stress, modulate cytokine production, and support overall vitality |
| Tinospora cordifolia (Guduchi) | Alkaloids, diterpenoid lactones, polysaccharides | They stimulate the activity of macrophages, boost antibody production, enhance resistance to infections, and reduce inflammation |
| Curcuma longa (Turmeric) | Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, turmerones | They act as anti-inflammatories, antioxidants that regulate cytokine production, enhance immune cell function, and fight infections |
| Panax ginseng | Ginsenosides, polysaccharides, peptides |
They enhance both innate and adaptive immunity, modulate cytokine levels, and improve resistance to infections. |
The bioactive compounds that are produced by the plant materials and plant extracts, which exhibit immunomodulatory properties, can be studied and investigated thoroughly because of advanced technologies in metabolomics, phytochemistry, and their analysis. The use of biotechnology will open a wide range of career opportunities and new avenues for improving immunomodulatory phytochemicals extracted from medicinal plants with regard to long-term use with safety and effectiveness.
Personalized medicines, in which plant extracts are customized to each individual’s immunological response, are one of the growing areas of future research. Additionally, interdisciplinary research combining immunology and phytochemistry is becoming more and more necessary in order to comprehend immune-regulating systems. Furthermore, interesting sources of new immunomodulatory chemicals with substantial therapeutic promise can be found in understudied plant materials.