Agrochemistry and Sustainable Agriculture: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Scope
The human population is expanding than ever before. As the population increases, so does the demand to feed that population. The biggest challenge is to ensure that the growing population is provided with healthy as well as nutritious food. Along with this, we are also responsible for ensuring a safe environment for the next generation. To achieve this, one should ensure that technological advancements are being incorporated into agricultural practices.
Hence, we should consider sustainable agricultural practices as the best possible way to make sure that the food quality is not compromised and to yield more nutritious food products for the general public. Advanced Agricultural techniques and new methodologies can help us achieve this goal of Sustainable and large food production.
This is where the agrochemistry actually plays a vital role. Agrochemicals not only help increase crop yield but also improve soil health.
Understanding Sustainable Agriculture
The goal of sustainable agriculture is to produce food that satisfies consumer demands while upholding strict nutritional and quality requirements. In addition, it guarantees that the same food can be created in the future without harming natural systems or sacrificing nutritional content. The first step in achieving this is the prudent management of natural resources, which helps avoid waste and overuse.
When we gradually reduce our reliance on dangerous chemicals, we can directly ensure that the ecosystem is being saved. And one of the biggest challenges in adapting to this is to maintain the crop yield. Multiple contemporary techniques, such as crop rotation, precision irrigation, and biologically inspired agricultural inputs.
The Role of Agrochemistry in Modern Farming
Agrochemistry can be termed as the integration of chemical products in agriculture. They can be either natural fertilizers or synthetic. Here, we observe that chemicals such as pesticides, herbicides, and other agents are present. These chemicals have indeed shown tremendous results in plant growth over many years. We can even consider them as friends to farmers. They have always helped the farmers in improving their crop yields. One more added advantage of these chemicals is that they have the ability to combat both biotic and abiotic stress.
However, traditional agrochemicals have side effects as well. The most common side effect is that they are the causative agents for soil and water pollutants. Apart from polluting the environment, they are also known to cause an ecological imbalance.
One of the other major concerns includes the negative impacts they pose on non-target organisms. All these criteria are the reasons that are driving farmers and researchers to move towards sustainable agriculture.
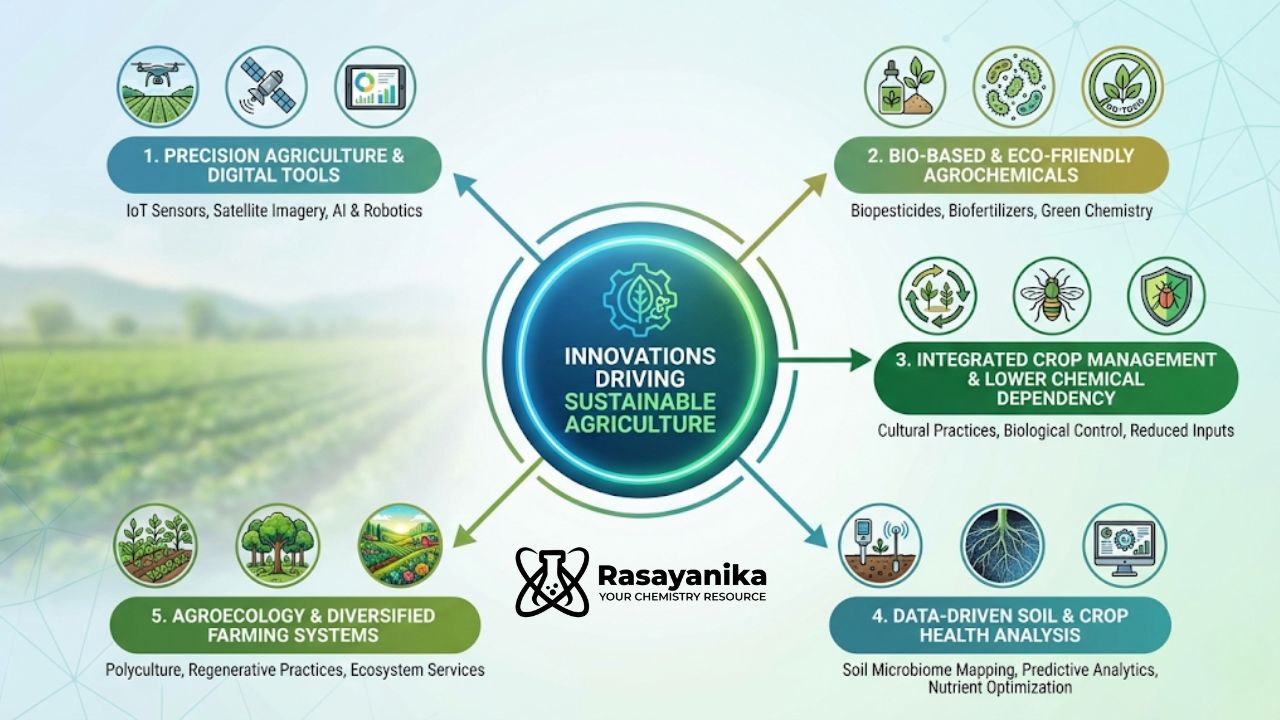
Innovations Driving Sustainable Agriculture
1. Precision Agriculture & Digital Tools
Precision agriculture is often considered the most widely adopted frontier of sustainable agricultural practices. With the help of data and AI, researchers are able to further improve and adopt new techniques. One of the most prominent examples of precision agriculture is the use of water and chemicals in a logical way. When chemicals are used at the right time and in the right amount, they have shown increased yielding results. The same applies to water as well. Watering crops can be optimised. Water, fertilizers, and pesticides are delivered to specific locations and at optimal times.
This not only ensures that resources are used efficiently but also helps reduce environmental stress from the overuse of chemicals and pesticides.
2. Bio-Based and Eco-Friendly Agrochemicals
Researchers have taken inspiration from nature. Nature already knew multiple ways to combat challenges and stressful conditions. Science and scientists are following these patterns, and the research is focusing more on the development of biopesticides, biostimulants, and biofertilizers. These not only ensure that the environment is on the safer side but also ensure that crops are devoid of chemicals. Thereby, it helps humans have a healthy consumption of food.
They can be considered as alternatives to regular fertilizers, and they are also extracted mainly from plant extracts. They align closely with the sustainable agriculture practices as per the motto.
3. Integrated Crop Management & Lower Chemical Dependency
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a strategy that combines biological, cultural, and chemical tools to manage pests. One of the main aims of IPM is to promote the ecological balance in the environment, especially in the soil and water, and also to limit the use of pesticides as much as possible.
By integrating biological control agents and crop monitoring systems, farmers can minimize the quantity of agricultural chemicals needed without sacrificing yields.
4. Data-Driven Soil and Crop Health Analysis
With the integration of AI in farming, one can understand the components present in the soil in a much faster and accurate way. The soil profiling could be much easier, and crop health can be monitored at the granular level. By ensuring the soil microbiome, one can easily observe the long-term effects on the soil and the need for less fertilizer in the upcoming years.
5. Agroecology and Diversified Farming Systems
Agroecology integrates ecological concepts with practical farming. Techniques such as crop diversification, cover cropping, and conservation tillage help enhance soil organic matter and reduce dependence on synthetic inputs, a significant pillar of sustainable agriculture.
Challenges at the Intersection of Agrochemistry and Sustainability
As we know, every coin has two faces; with so many advantages come the disadvantages and challenges too.
Environmental and Regulatory Pressures
When there are multiple regulations imposed to maintain and protect the ecosystems, various chemical compounds are being eliminated from the market. But this does not stop the manufacturer from thinking less; they are given one more chance to innovate and come up with more such chemicals, which will help in crop yields. This will further lead to more costly products and complex agricultural chemicals being introduced into the market.
Farmer Adoption and Economic Constraints
As most of the farmers are unaware of technological advancements as well as reluctant to adopt new techniques, it will become a hurdle in the shift towards sustainable agriculture. Most of the agrochemical solutions require a huge amount of capital as well and put the farmers in a fix to invest in such techniques. Small-scale farmers might not adapt to such innovations, and this could become a potential barrier in slowing down the shift towards sustainability.
Resistance and Pest Challenges
As pesticides have been a core component of agricultural practices, there has been a significant increase in resistant strains of these pathogens over the years. This, in turn, makes the already existing chemicals less effective and requires advanced, targeted agrochemical solutions.
The Future Scope of Agrochemistry in Sustainable Agriculture
The next decade promises a landscape transformed by science and sustainability:
Integration with Digital and Biological Technologies
There should be a constant effort in coupling agrochemistry with digital agriculture and biological innovations. This will be a crucial step as it will offer precision solutions that respect both ecological systems and farmer livelihoods.
Expanding Bio-Based Markets
As sustainable farming principles become mainstream, the market for eco-friendly agricultural inputs is poised for exponential growth. This shift encourages the development of products that are both effective and in harmony with nature.
Interdisciplinary Research and Sharing Knowledge
The movement toward sustainable agricultural practices has already led to a very noticeable shift in the globe’s scientific cooperation in agrochemical research. The core of that work is the invention and application of eco-friendly molecules. Besides, the major efforts are also aimed at determining the most suitable delivery systems, which will continue to influence the adoption of sustainable farming practices.
The path to agricultural sustainability is a movement that has many twists and turns, but it truly is one of the essential ones. The acceptance of bio-based inputs, precision technologies, and integrated farming systems will enable agriculture to reach the same or even a higher level of output without causing any harm to the earth.
The partnership between sustainable methods and chemical science will predict the world’s capability of feeding itself today and tomorrow in the face of climate change, population increase, and ecological bounds.