Table of Contents
What is Analytical Chemistry? A Complete Guide for Students and Professionals
Analytical chemistry is one of the most fascinating branches of chemistry. It mainly aims to analyze different types of substances. This acts as a foundational branch of chemistry through which numerous discoveries in pharmaceuticals, environmental science, food quality, and even space exploration have been made.
This branch of chemistry not only helps in identifying substances in the laboratory, but it is also the science of understanding matter. The domain extensively helps in determining composition and ensuring accuracy in every measurement that drives modern research and industry.
This article helps readers like you understand and explore analytical chemistry in detail, including its primary techniques, real-world examples, and its growing scope for students and professionals.
Understanding Analytical Chemistry
At its core, the branch of chemistry that focuses on identifying the components of a material (qualitative analysis) and determining the amount of each element present in it (quantitative analysis).
This particular branch of chemistry helps in answering two simple yet powerful questions. The first question is, what is this substance made up of? And the second is how much of each part is present in that particular sample?
According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), analytical chemistry deals with the “development and application of methods and instruments for obtaining information about the composition and structure of matter.” This is one of the main reasons why analytical chemistry is used in every field of science.
Branches of Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry is typically divided into two main branches:
- Qualitative Analysis: This deals with the determination of what types of substances are present in the sample. For example, one can detect toxic metals like lead or mercury in water samples.
- Quantitative Analysis: This helps in determining how much of a substance is present. For example, we can easily determine the blood sugar levels or carbon dioxide levels present in the air.
Beyond these, the branch is also categorized based on the techniques used:
- Classical methods: Include titration, gravimetry, and precipitation.
- Instrumental methods: Include spectroscopy, chromatography, and mass spectrometry, highly advanced techniques that provide accurate and detailed results.
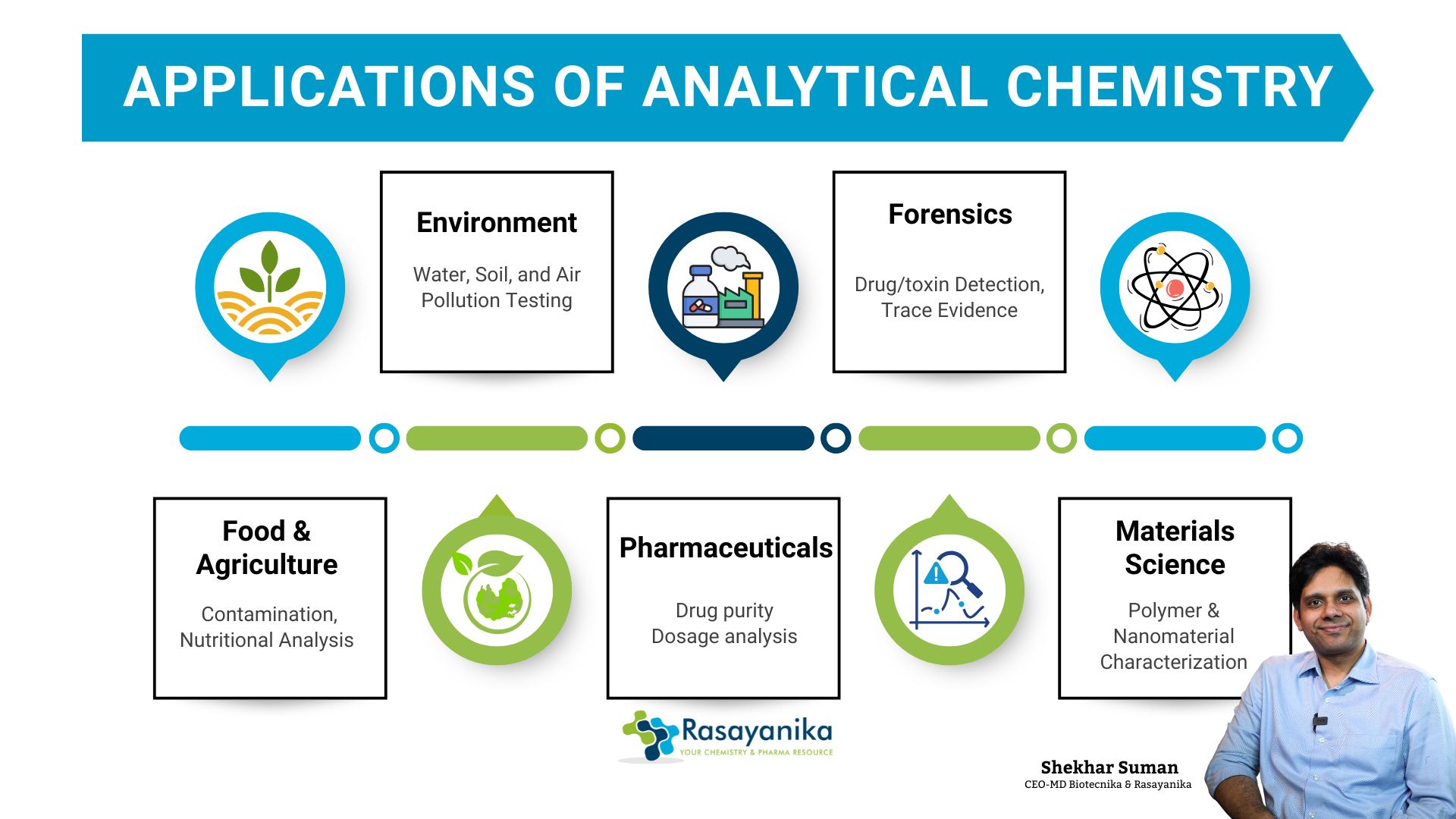
Applications of Analytical Chemistry
1. Pharmaceuticals
In drug development, analytical chemistry ensures the purity, safety, and efficacy of medicines. The drugs are checked for their purity through different techniques such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Mass Spectrometry (MS). They are extremely effective in detecting the impurities present in the drug samples.
2. Environmental Monitoring
Analytical chemists measure pollutants in air, water, and soil to ensure environmental safety and health. For example, Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) helps detect trace pesticides or volatile organic compounds in water.
3. Food and Agriculture
Analytical chemistry plays an important role in identifying adulterants present in food samples. This will aid in ensuring quality checks through nutritional labeling, pesticide residue detection, etc. This is one of the best examples of analytical chemistry techniques used in daily life.
4. Forensic Science
From blood analysis to toxicology reports, analytical chemistry techniques help solve crimes by identifying unknown substances and linking evidence to individuals.
5. Energy and Materials
In energy research, analytical chemistry plays a crucial role in studying new materials for batteries, fuel cells, and catalysts used in renewable energy technologies.
Examples of Analytical Chemistry in Everyday Life
Analytical chemistry may sound complex, but its influence surrounds us in everyday scenarios.
Here are a few examples;
- Blood tests: The techniques help in quantifying the level of glucose or cholesterol present in samples for medical diagnosis.
- Water purification: one of the widely used applications of analytical chemistry is the detection of heavy metal contamination in water before the public supply.
- Food safety testing: Ensuring packaged foods are free from harmful additives.
- Cosmetic analysis: the techniques used in analytical chemistry help in the verification of cosmetic products and ensure that they contain approved ingredients.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Validating that every tablet or vaccine meets quality standards.
These real-world examples highlight how they bridge the gap between science and human well-being.
Must know Primary Analytical Techniques
Analytical chemistry encompasses a range of sophisticated techniques. These techniques are extensively used to extract reliable information from samples. Some widely used methods are listed below:
- Spectroscopy: This technique is widely used in studying how matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation. For example, it is used along with UV-Vis, IR, and atomic absorption spectroscopy.
- Chromatography: Separates components of a mixture. Techniques include Gas Chromatography (GC) and Liquid Chromatography (LC).
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): Determines molecular weight and structure of compounds.
- Electrochemical Analysis: This includes potentiometry and voltammetry, which are used in sensors and industrial monitoring.
- Thermal Analysis: Evaluates material stability and decomposition under heat.
Each technique offers unique insights that help the researchers and chemists to detect even trace amounts of substances with high accuracy.
Scope of Analytical Chemistry
It ensures the utmost safety of drug candidates. This is achievable due to the advanced techniques used in identifying and detecting the impurities and thereby increasing the accuracy of tests. Due to which we can also observe a huge career opportunity in career paths.
Analytical chemists have high career opportunities in the following domains:
- Pharmaceutical companies (for quality control and formulation)
- Environmental laboratories (for pollutant analysis)
- Food and beverage industries
- Forensic departments
- Research organizations and academic institutions
Emerging Research Fields
The future of analytical chemistry holds promising career opportunities in various fields such as:
- Nanomaterial analysis – here, one studies materials at the nanoscale.
- Green analytical chemistry – the area deals with designing sustainable, eco-friendly analytical methods.
- Bioanalytical chemistry – this domain integrates biology and chemistry for medical diagnostics.
- Automation and AI-assisted analysis – enhancing data accuracy and interpretation.
With the world’s growing emphasis on data reliability and safety, the scope of analytical chemistry continues to rise, offering stable, rewarding, and globally relevant career paths.
FAQs
- What is analytical chemistry used for?
Analytical chemistry is used to determine the composition and quantity of substances in a sample. It supports industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, environmental science, and materials science. - What are the primary methods used in analytical chemistry?
Standard techniques include spectroscopy (UV-Vis, IR, AAS), chromatography (HPLC, GC), titration, and mass spectrometry. - What is an example of analytical chemistry in daily life?
Testing the amount of caffeine in coffee or detecting pollutants in drinking water are practical examples of analytical chemistry in action. - What is the scope of analytical chemistry as a career?
The scope of analytical chemistry is broad. Graduates can work in R&D, quality control, forensic labs, pharmaceutical manufacturing, or pursue research and teaching careers. - How is analytical chemistry different from physical chemistry?
While physical chemistry focuses on energy changes and molecular interactions, analytical chemistry deals primarily with identifying and quantifying substances.