Table of Contents
Emerging Materials & Nanotechnology Trends Every Chemist in India Should Know
Can you imagine holding a material so thin that you can see through it, yet it is stronger than steel, which can conduct electricity better than any copper wire? Or think of a particle smaller than your hair cells that is carrying medicines directly to diseased cells. These are not just some science fiction but are actually happening in India because of the rise of nanomaterial chemistry in India. In the labs of IITs, IISc, and CSIR research centers & Universities, where people are working on projects like this.
With the growing technology and advanced materials research in India, the world of nanomaterials chemistry in India is blooming and transforming industries and everyday life. Recently, researchers have invented graphene based batteries, quantum dot LEDs, and other semiconductor devices, which is a result of decades of work by many organizations and contributors. In India, researchers are turning ideas into actual products, and the se innovations are the growing focus on advanced materials research in India because they are shaping the materials chemistry trends in 2025.
The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has played a central role by launching the Nano Mission. The DST is funding the research labs to support advanced instruments and has created a network between IITs, IIScs, CSIR Institutes, and industry partners.
In this article, we will discuss the emerging materials and nanotechnology trends in India 2025.
R&D Strength in Advanced Materials in India
Academic Institutions
IISc Bangalore:
Scientists are working on solid-state batteries, which are safer and have high energy, advanced 2D materials like graphene, and nanofabrication, which is developing extremely small devices and structures.
IIT Bombay:
It is well known for graphene research, and they are developing new battery materials and conducting studies to improve energy storage and create polymer nanocomposites in which a plastic is mixed with nanoparticles to give them a robust structure or smarter properties.
IIT Madras:
This institute focuses on perovskite solar materials, that is next gen solar cells, biomaterials for healthcare, and membrane materials for clean water technologies.
IIT Delhi & IIT Kanpur:
They work on nanoelectronics; tiny electronic devices, biosensors, quantum dots, and semiconductor materials for modern electronics.
National Research Labs
- CSIR labs: NCL Pune is working on catalysis and nanomaterials that would help chemical reactions become faster and cleaner. CECRI specializes in electrochemical materials like batteries, fuel cells, and coatings, and NEERI Institute uses nanotechnology to make membranes to solve environmental problems.
- ARCI Hyderabad: They are focusing on nanocoatings, ceramic materials, and engineered surfaces that are used in aerospace, automotive, and energy applications.
- SERB/DST Centres are government-funded research centres that support nanoscience by providing equipment. It also promotes collaboration among other institutes.
Industry and Startups
Recently, many new startups in India have been working on Graphene products, energy storage technologies, semiconductor materials, and nano-biotech products. These start-ups are in collaboration with IITs and IIScs.
What are the emerging materials in India (2025)
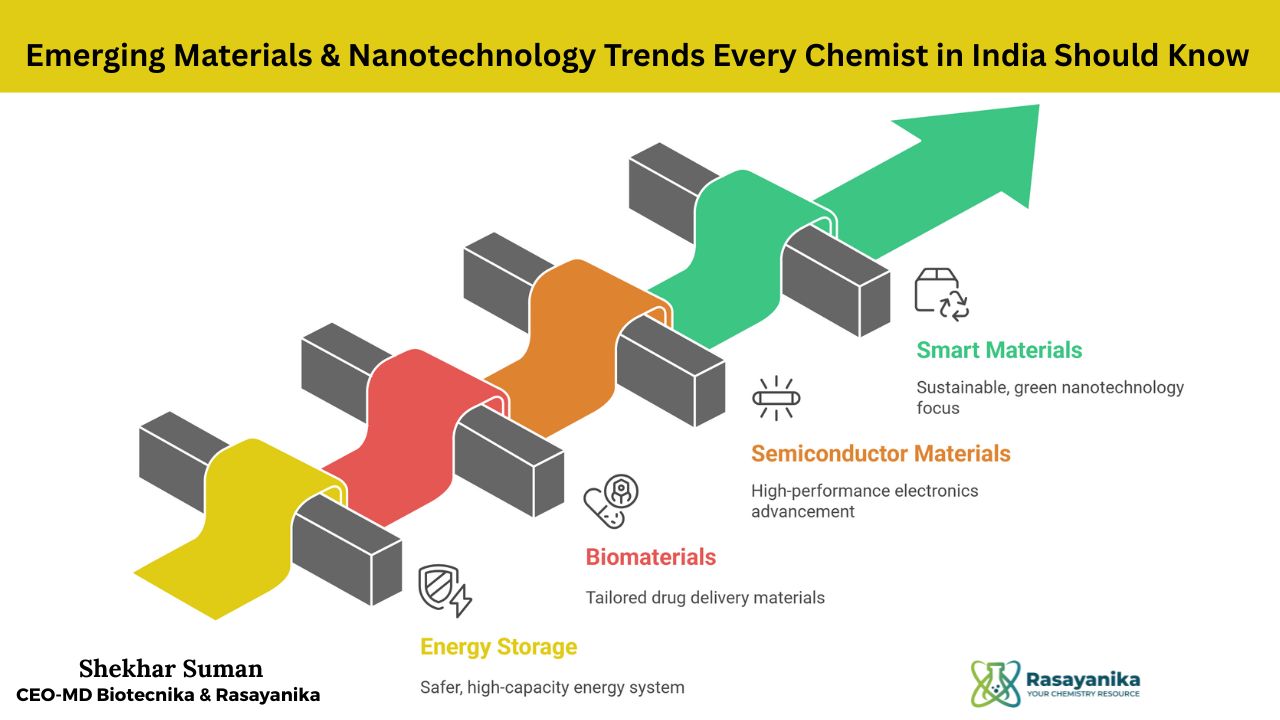
Energy Storage Materials:
India is advancing rapidly in sodium-ion and lithium sulfur batteries research, which is supported by innovations such as graphene electrodes, solid-state electrolytes, and ceramic conductors. IISc, IIT, and CECRI are the leading breakthroughs that aim for a safer energy system with high capacity.
Biomaterials:
Materials like biodegradable polymers, hydrogels, lipid nanoparticles, and antimicrobial nano coatings are firmly attracting the healthcare and diagnostics. Institutes such as IIT Guwahati, IIT Kharagpur, and IISERs are developing biosensors and materials that are tailored to deliver drugs in medical applications.
Semiconductor Materials:
Currently, India is emphasizing 2D semiconductor materials, GaN, SiC, and Perovskite films for high-performance electronics. This is supported by the India Semiconductor Mission and CeNSE at IISc, and these materials allow advanced sensors, optoelectronic devices, and solar technologies.
Smart & Sustainable Materials:
Initiatives are taken for developing and designing self-healing polymers, conducting polymers, and materials that can respond to smart devices. The researchers are raising interest in the waste of graphene and recyclable nanocomposite materials, highlighting India’s focus on sustainable and green nanotechnology for manufacturing materials.
Industry Applications in India
- Energy storage products: Such as graphene-based batteries and supercapacitors.
- Nanoformulated pharmaceuticals: nanoformulated drugs and lipid nanoparticles are enabled to target the drug delivery system and improve the bioavailability of drugs.
- Nanocoatings for corrosion protection: Nanocoatings are used to apply in infrastructures, automatic components, and industrial machinery to enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs.
- Agricultural nanomaterials: Slowly releasing nano fertilizers to improve nutrient efficiency and monitor with nano sensors to optimize soil health, yield, etc.
- Water purification membranes: nano catalysts are developed to remove contaminants like pathogens or heavy metals. It also enhances the efficiency of water treatment for industrial and domestic applications.
Challenges for Materials Chemistry in India
- It is difficult to produce nanoparticles at an industrial scale while maintaining the quality consistently.
- There is still a lack of uniform standards and safety frameworks for the commercialization of nanomaterials and their handling.
- The ability to produce high-purity, semiconductor-grade material is limited in India for advanced electronics.
- There is a lack of advanced tools and facilities for the analysis, validation, and optimization of nanomaterials and other advanced materials.
Advanced materials research in India in the nanotechnology sector has witnessed remarkable progress over the past few years. From 2D materials, quantum dots, and work in graphene to innovations in energy storage materials, biomaterials, and semiconductors, India has demonstrated the ability of its researchers and Institutions like IITs, IIScs, etc, to transform science and technology into practical and real applications in sectors such as healthcare, electronics, agriculture, energy, and environmental sustainability.
To completely capitalize on these advancements, there is a significant need for upskilling the workforce in the new technologies, such as nanomaterial synthesis, computational materials science, and AI-driven materials discovery.
The nanomaterials revolution is not just a frontier but a launchpad for chemists and researchers to shape the future of technology.