The Hidden Chemistry of Vaccines: How Do Vaccines Work?
I am sure all of you must have finished your preparatory exams and are now ready for your Mains. What exactly happened when you wrote those Preparatory is that you were trained to do well in the actual exam. The same analogy works for Vaccines.
Everyone understood the power of Vaccine development, once the world faced waves of Covid after 2020. They are one of the most powerful tools when th world as a whole faced a near-death experience. Only because of vaccines, millions of lives been saved all over the world. We can just call them the molecular heroes of our lives. One of the very first vaccines produced was out of accidents, and with the advancement of science and technology, researchers are striving to develop as many vaccines as possible.
Yet, for many people, the science behind them remains a mystery. What exactly happens inside the body after a vaccine shot? How does a tiny dose of biological material create long-lasting protection? All this is highly interesting, and everyone should know about how these miraculous molecules are helping humanity.
This article will help in understanding the chemistry as well as the biology behind the Vaccines in detail.
The Immune System: Your Body’s Built-In Defense Lab
Before understanding vaccines, it is essential to understand the immune system. Think of it as a highly advanced chemical and biological defense laboratory operating inside your body 24/7. It identifies foreign invaders, studies them, and designs precise molecular weapons, which we generally call antibodies, to neutralize them.
When a virus or bacterium enters the body for the first time, the immune response from the body will be slow. There is a series of events that will occur inside the cells, and Special cells called antigen-presenting cells capture pieces of the pathogen and display them to helper T-cells. These activate B-cells, which begin producing antibodies. Over time, these immune cells become memory cells. The memory cells are our true warriors, capable of remembering what attacked the body and what the consequence was. When this recognition is quick, the body is ready to fight back quicker. Thereby, saving the lives. This biological memory is the foundation of vaccination science. This is how the Vaccine mechanism of action works.
The Central Principle Behind Vaccination
To curate in a much simpler way, we can say that vaccines are like a training program that is conducted for the immune system of our body. Vaccination is mainly done to prevent the hazardous effects of direct encounter with pathogens. The vaccine helps in remembering the pathogen part of th whole pathogen and the body to be prepared.
Vaccines are helping in understanding the actual pathogens even before the encounter of the actual pathogen. The immune cells in the body will study the structure of pathogens and remember them. And when they are ready with those memory cells, they can easily fight back the infection or diseased conditions.
The Chemistry Inside a Vaccine Dose
A vaccine is not just one ingredient; it is a carefully engineered chemical formulation. Each component plays a precise role: let us understand in detail the ingredients of a Vaccine.
- Antigens: These are weakened, inactivated, or fragmented parts of viruses or bacteria. They are the most essential part of the vaccine as they help trigger a specific immune response inside the body.
- Adjuvants: Substances like aluminum salts that boost immune reaction and improve long-term protection. They are like supporting materials.
- Stabilizers: Sugars or proteins that protect the vaccine during storage and transport.
- Preservatives: As the name suggests, they help in preventing the vaccine product from any kind of contamination, such as microbes.
Together, these ingredients form a delicate chemical balance designed to be safe, stable, and highly effective.
Different Types of Vaccines and Their Chemistry
Not all vaccines are made the same way. There are multiple ways and techniques to produce and store vaccines. Advances in biotechnology have introduced multiple vaccine platforms, each with unique chemical and biological behavior:
1. Live Attenuated Vaccines
These contain weakened versions of the pathogen. They closely mimic natural infection and often provide lifelong immunity after one or two doses.
2. Inactivated Vaccines
This type of vaccine is produced when the pathogen is chemically killed using heat or chemicals such as formaldehyde. These vaccines are safe, as the pathogen is not in its active state, but has the necessary capabilities to trigger the specific immunity inside the body
3. Subunit and Conjugate Vaccines
This type of vaccine is particular as it holds specific protein fragments or sugars of the pathogens. They are particular and precise in their nature.
4. mRNA Vaccines
These deliver genetic instructions that teach human cells to produce a harmless viral protein, prompting immunity temporarily. This approach revolutionized modern vaccine science.
Each of these platforms plays a role in modern vaccine development, allowing scientists to rapidly respond to emerging diseases.
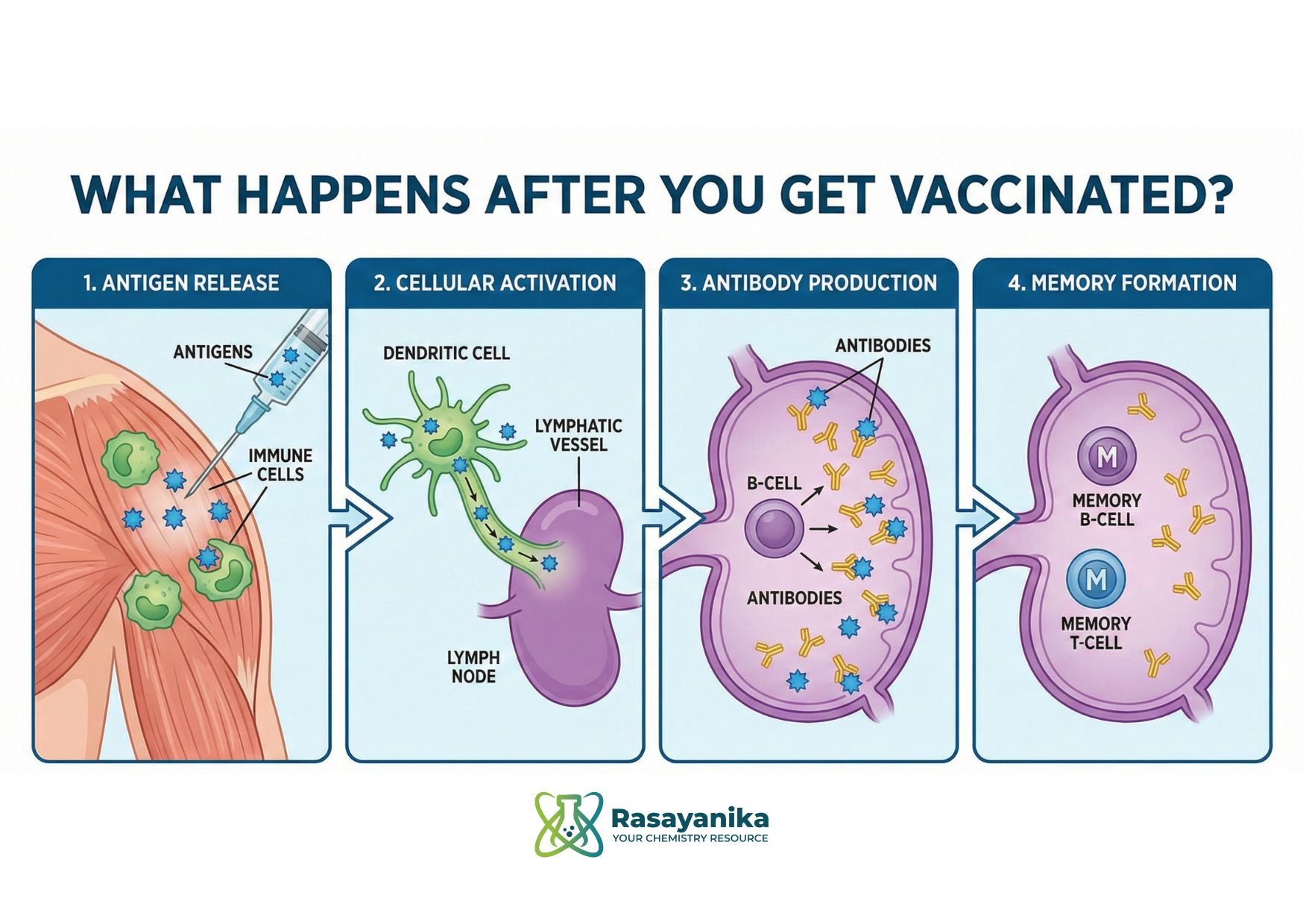
What Happens After You Get Vaccinated?
Once the vaccine enters your body, the chemistry immediately begins to unfold:
Why Vaccines Do Not Cause the Disease They Prevent?
A common concern is whether vaccines can cause infection. The answer is no, because the disease-causing ability has been removed or weakened beyond harmful levels. Even mRNA vaccines do not enter the nucleus and cannot alter human DNA. The protein they produce is harmless and disappears within days.
What remains is immune memory. Our body can build that personalized defense blueprint.
Beyond Individual Protection: Community-Level Safety
Vaccines not only protect an individual but also the entire community. When a large population is immunized with vaccines, the spread rate of infectious diseases is known to be drastically reduced. When this happens, it is termed herd immunity. This plays a significant role in building immunity in the entire community. This is achieved because it helps protect the newborn, as they cannot be directly vaccinated. The same applies to elderly people. As they already have a weakened immune system, it is advised that they achieve herd immunity. This includes patients under chemotherapy as well as individuals who possess genetic immune disorders.
Artificial intelligence and computational chemistry are accelerating antigen discovery, enabling faster vaccine responses than ever before.
Just like those preparatory exams you took before taking the actual exams. They quietly train your immune system, protect entire communities, and save lives every single day. Understanding how vaccines work empowers people to make informed decisions, trust science, and appreciate one of humanity’s most significant medical achievements.